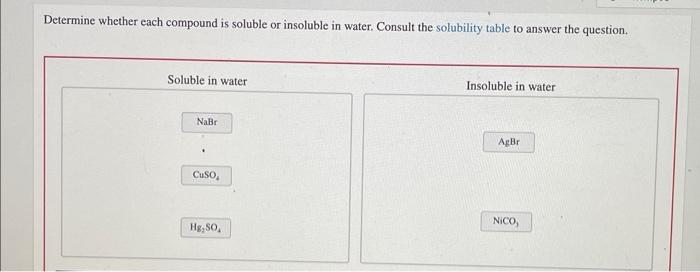
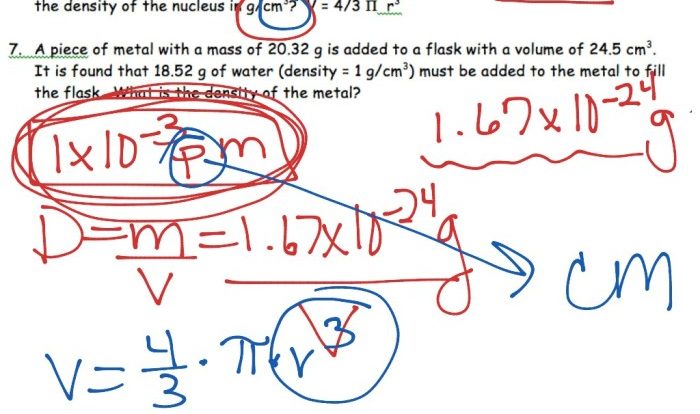Determine whether each compound is soluble or insoluble in water. – Understanding the solubility of compounds in water is a fundamental aspect of chemistry, with far-reaching applications in various scientific disciplines and everyday life. This guide delves into the concept of solubility, exploring the factors that influence it and providing a systematic approach to determining whether a compound is soluble or insoluble in water.
Understanding Solubility
Solubility refers to the ability of a compound to dissolve in a solvent. Water is a common solvent, and the solubility of a compound in water depends on its chemical structure and properties. Factors that influence solubility include polarity, hydrogen bonding, and molecular weight.
Polarity
Polarity refers to the uneven distribution of electrical charge within a molecule. Polar molecules have a positive end and a negative end, and they tend to be soluble in polar solvents like water. Nonpolar molecules, on the other hand, have a uniform distribution of electrical charge and are generally insoluble in water.
Hydrogen Bonding, Determine whether each compound is soluble or insoluble in water.
Hydrogen bonding is a type of intermolecular force that occurs between molecules that have hydrogen atoms bonded to highly electronegative atoms, such as oxygen or nitrogen. Hydrogen bonding can increase the solubility of a compound in water because it forms attractive forces between the compound and the water molecules.
Molecular Weight
In general, compounds with higher molecular weights are less soluble in water than compounds with lower molecular weights. This is because larger molecules have more surface area and are less able to penetrate the water molecules.
Identifying Soluble and Insoluble Compounds
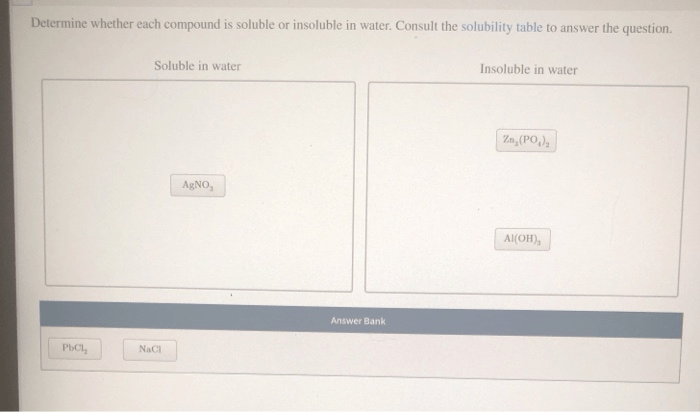
Soluble Compounds
Soluble compounds are those that dissolve in water to form a homogeneous solution. They are typically polar or ionic compounds, and they have a strong affinity for water molecules.
Insoluble Compounds
Insoluble compounds are those that do not dissolve in water to any significant extent. They are typically nonpolar compounds, and they have a weak affinity for water molecules.
Determining Solubility: Determine Whether Each Compound Is Soluble Or Insoluble In Water.

Experimental Methods
The solubility of a compound can be determined experimentally by performing a solubility test. In a solubility test, a known amount of the compound is added to a known amount of water, and the mixture is stirred until equilibrium is reached.
The amount of compound that dissolves is then measured, and the solubility is calculated.
Factors to Consider
When determining the solubility of a compound, it is important to consider factors such as temperature and pH. Temperature can affect the solubility of a compound because it changes the kinetic energy of the molecules. pH can affect the solubility of a compound because it can change the charge of the compound.
Practical Applications
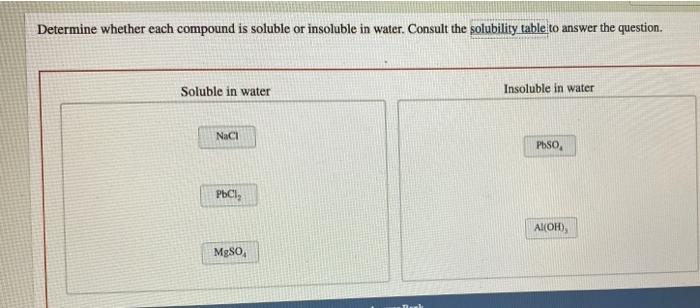
Understanding solubility is important in a wide range of fields, including chemistry, medicine, and environmental science. In chemistry, solubility is used to separate and purify compounds. In medicine, solubility is used to determine the bioavailability of drugs. In environmental science, solubility is used to assess the fate and transport of pollutants.
FAQs
What factors affect the solubility of a compound in water?
Polarity, hydrogen bonding, and molecular weight are key factors that influence the solubility of a compound in water.
How can I experimentally determine the solubility of a compound?
Solubility tests and observations can be used to experimentally determine the solubility of a compound in water.
What are the practical applications of understanding solubility?
Understanding solubility has applications in chemistry, medicine, environmental science, and various industrial processes.